2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第一场)C Euclidean Distance
题解: 拉格朗日乘子法,首先引入拉格朗日乘子得出公式
这个应该看的懂,然后引入对偶变成成其中
然后化成叉姐给的题解里面的公式就行了
再然后,我就不会了qaq
后来看了一下别的大佬的博客,突然感觉可以直接理解一下,
假设所有的$p_i=0$,$f(x)$就等于$a_i^2$的和
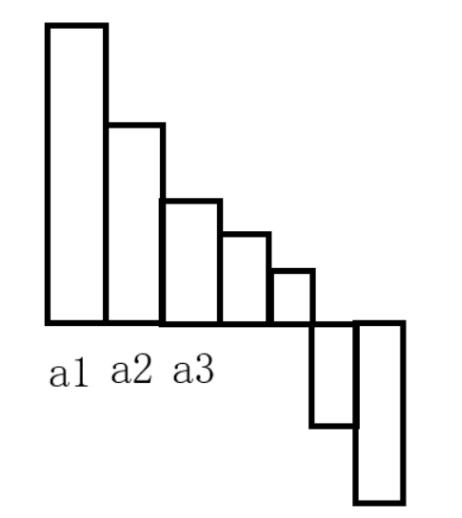
题目要求的是 在
条件下求 $f(x)=\sum_{i=1}^{n}(p_i-a_i)^2$ 。相当于分配$p_i$ 的值,去让 $(p_i-a_i)^2$ 变小。
根据二次函数的性质,自变量 $x$ 越大因变量 $y$ 化越快。所以先分配给最大肯定更优啊,直接贪心下去啊。最后肯定是变成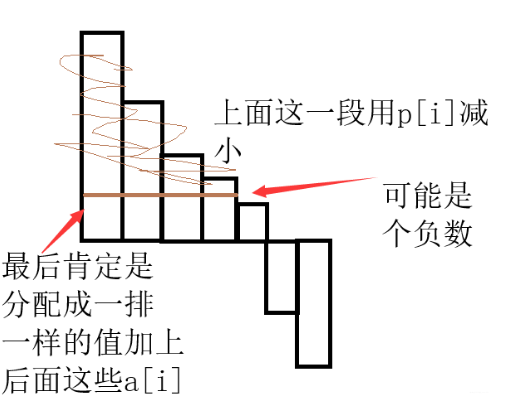
1 |
|