A - Tokitsukaze and Enhancement
简单题不与说明1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
const long long mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int INF=0x7fffffff;
const LL inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps=1e-8;
void f() {
freopen("dat.in", "r", stdin);
}
int main() {
f();
int x;
cin>>x;
x=x%4;
if(x==0) {
printf("1 A\n");
} else if(x==1) {
printf("0 A\n");
} else if(x==2) {
printf("1 B\n");
} else printf("2 A\n");
return 0;
}
B - Tokitsukaze and Mahjong
1 |
|
C - Tokitsukaze and Discard Items
1 |
|
D - Tokitsukaze, CSL and Stone Game
首先这题是简单粗暴,因为选择到两个相同的就输了,说明每一个都不相同,最终状态肯定是 0 1 2 3 …. n-1
这种状态肯定是必输,无法动弹。所以最终都会变成这个状态,判断一下到这个状态的奇偶就是答案。
另外还有一开始就输了的状态,比如 3 4 4 两个一样的,只能选一样的,但是选了有一个和他相同,还有 0 0 一开始就有两个0 还有就是 5 5 5 三个一样的或者两对两个一样的,这四种状态绝对是直接输了。
1 | By ET_BUBBLE, contest: |
F - Tokitsukaze and Strange Rectangle
题意:自己读去
题解:先按照,y从大到小排序在按照x从小到大排序,然后每次判断一层y。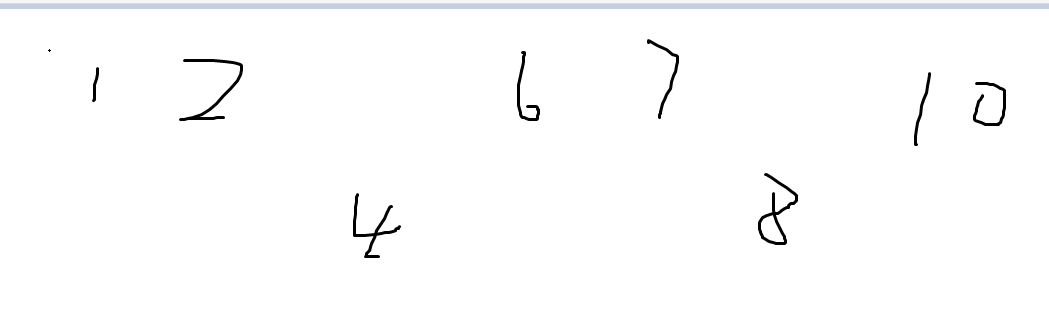
先判断第一层 1 2 6 7 10 (假设)y=10
然后判断第二层 4 8 (假设) y = 9
第一层能够出现的不同的选法是 5*(5-1)/2;
第二层会受到第一层的影响 1 2 在 4 前面,所以
要选 4 的矩形情况 是
红色l到右边蓝色r的所有矩形,会选上4,同理选上8又不和前面的重复就只能是这样了。
然后又可以发现,如果有第3层 ,前面两层对第3层的影响只与x的出现有关,每次判断一层只需要考虑上面出现的 x
的影响。
先离散化一下,然后用树状数组求一下这个点前面有多个点,后面有多少个点,然后乘一下就可以了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
const long long mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int INF=0x7fffffff;
const LL inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps=1e-8;
void f() {
freopen("dat.in", "r", stdin);
}
int bit[maxn+1],pos;
int sum(int i) {
int s=0;
while(i>0) {
s +=bit[i];
i-=i&-i;
}
return s;
}
void add(int i,int x) {
while(i<=pos) {
bit[i]+=x;
i+=i&-i;
}
}
int n;
struct node {
int x,y;
} p[maxn];
bool cmp(node &o1,node &o2) {
if(o1.y==o2.y)return o1.x<o2.x;
return o1.y>o2.y;
}
LL ans=0;
unordered_map<int,int>mp;
int a[maxn];
int main() {
f();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
a[i]=(p[i].x);
}
pos=1;
sort(a,a+n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if(i==0) {
mp[a[0]]=pos++;
} else if(a[i]!=a[i-1]) {
mp[a[i]]=pos++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
p[i].x=mp[p[i].x];
}
sort(p,p+n,cmp);
int len=0;
a[len++]=p[0].x;
add(p[0].x,1);
int mx=pos;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++) {
if(p[i].y==p[i-1].y) {
a[len++]=p[i].x;
if(sum(p[i].x)-sum(p[i].x-1)==0)add(p[i].x,1);
} else {
int la=0;
// sort(a,a+len);
for(int j=0; j<len; j++) {
int i=a[j];
ans+=1LL*(sum(i)-sum(la))*(sum(mx)-sum(i-1));
la=i;
}
len=0;
a[len++]=(p[i].x);
if(sum(p[i].x)-sum(p[i].x-1)==0)add(p[i].x,1);
}
}
int la=0;
// sort(a,a+len);
for(int j=0; j<len; j++) {
int i=a[j];
ans+=1LL*(sum(i)-sum(la))*(sum(mx)-sum(i-1));
la=i;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}